ReasonScape¶
ReasonScape is a research platform for investigating how reasoning-tuned language models process information.
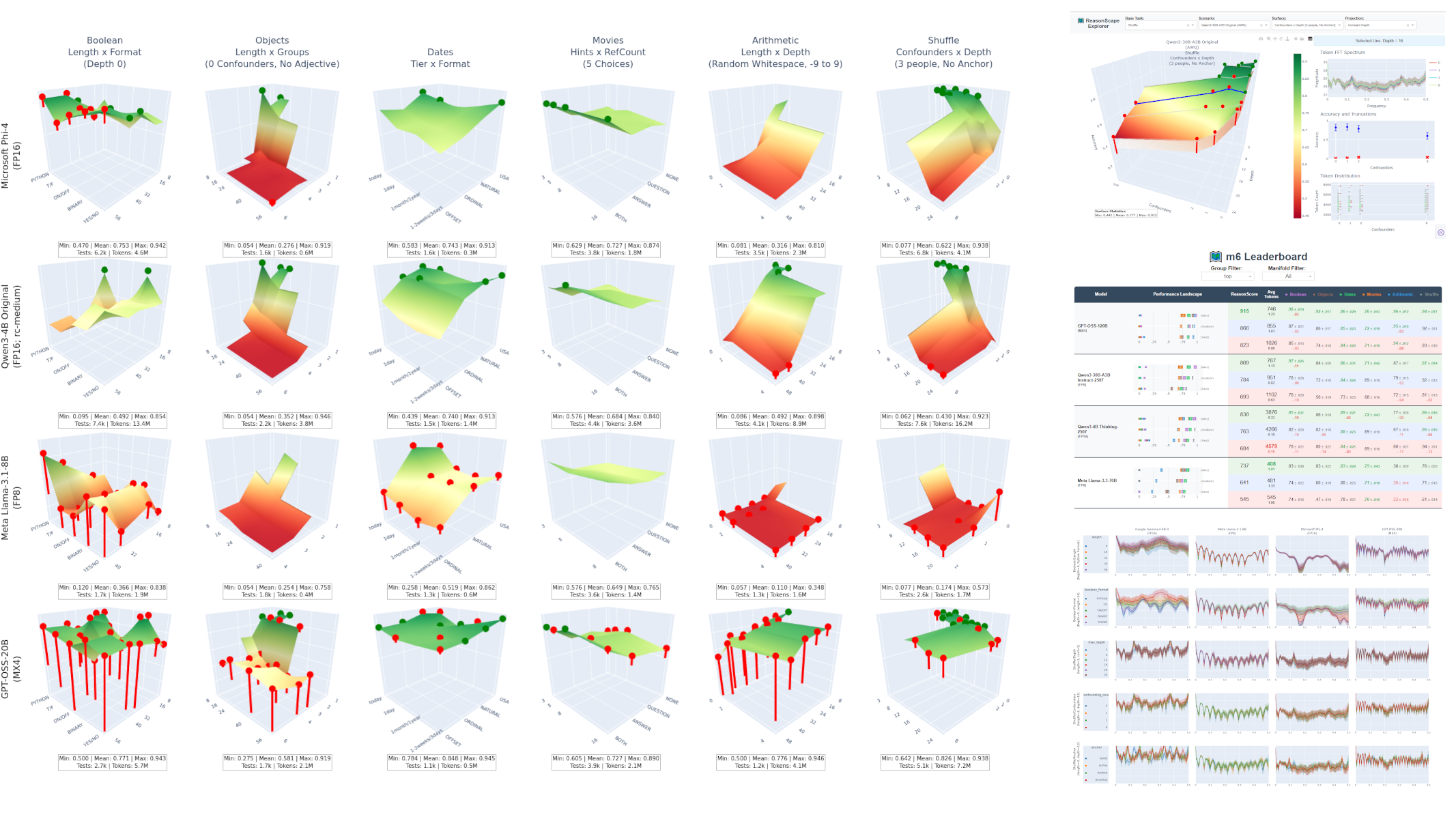
ReasonScape reveals cognitive architecture patterns invisible to traditional benchmarks: 3D reasoning landscapes (left), token-frequency spectral analysis (bottom right), and interactive exploration tools (top and middle right) enable systematic comparison of information processing capabilities across models and tasks.
🌐 Homepage: https://reasonscape.com/
🛠️ GitHub: the-crypt-keeper/reasonscape
Keywords: Large language models, AI evaluation, cognitive architectures, spectral analysis, statistical methodology, parametric testing, difficulty manifolds, information processing
Live Tools & Data¶
📊 Visualization Tools:
-
M12X Leaderboard: https://reasonscape.com/m12x/leaderboard
-
M12X Explorer: https://reasonscape.com/m12x/explorer (PC required)
📁 Raw Data:
- M12X Dataset: https://reasonscape.com/data/m12x (75+ models, 6.5B tokens)
The Six Pillars of ReasonScape¶
The ReasonScape project is multi-faceted, the documentation is logically organized into six "pillars":
| Pillar | What It Is | Where to Learn More | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Challenges | Practical problems encountered in prior LLM evaluation systems | challenges.md |
| 2 | Insight | LLMs are not simply text generators, they're information processors | insight.md |
| 3 | Methodology | Systematic solutions that emerge from applying the Insight to the Challenges | architecture.md |
| 4 | Implementation | The Python codebase that makes it real | implementation.md |
| 5 | Reference Evaluation | m12x as proof the methodology works | m12x.md |
| 6 | Research Datasets | Worked examples showing the methodology in action | datasets.md |
These "pillars" support each other: The challenges lead to the the insight. The methodology applies the insight to solves the challenges, grounded by implementation. The reference evaluation proves the implementation works. The insight is validated by billions of tokens of research dataset evidence.
Where to Start¶
Understand the Vision¶
Challenges - The problem statement (Pillar 1)
- 6 fundamental challenges in current LLM evaluation
- Practical barriers encountered in prior systems
Insight - The paradigm shift (Pillar 2)
-
LLMs as information processors
-
System architecture and transformation pipeline
Architecture - The methodology (Pillar 3)
- Applies the Insight to the Challeneges
- Five-stage data processing pipeline
- Discovery-investigation research loop
Use the Datasets¶
m12x - The reference evaluation (Pillar 5)
- 75+ models, 12 reasoning tasks, 6.5B tokens
- Proof that methodology works at scale
- Quick start guide and configuration details
Datasets - Research collections (Pillar 6)
- Main m12x + 7 research subdatasets
- Worked examples of complete investigations
- Templates for your own research
Workflow Guide - Four research patterns
- Ranking & Benchmarking
- Comparative Evaluation
- Model Characterization
- Failure Diagnosis
Dive Deeper¶
Implementation - The Python codebase (Pillar 4)
- Stage-by-stage implementation guide
- Deep-dive design documents (manifold, reasonscore)
- Tool references and workflows
Technical Details - Low-level algorithms
- Parametric test generation
- Statistical methodology
- FFT analysis and compression
Tools - Complete tool reference
- analyze.py forensic toolkit
- Leaderboard, spider plots, explorer
- runner.py and evaluate.py
Config - Configuration reference
- Templates and samplers
- Manifolds
- Dataset format
Datasets - Main and research datasets (Pillar 6)
- Dataset taxonomy and lifecycle
- 7 worked research examples
- Graduation patterns
PointsDB - Data structure API
Tasks - Abstract task API and task overview
- tasks/*.md - 12 individual task specifications
Citation¶
If you use ReasonScape in your research, please cite:
@software{reasonscape2025,
title={ReasonScape: Information Processing Evaluation for Large Language Models},
author={Mikhail Ravkine},
year={2025},
url={https://github.com/the-crypt-keeper/reasonscape}
}
License¶
MIT
Acknowledgments¶
ReasonScape builds upon insights from BIG-Bench Hard, lm-evaluation-harness, and the broader AI evaluation community.