LLM evaluation that considers how models think.
ReasonScape treats LLMs as the Information Processing Systems they are - adressing blind spots of static benchmarks with parametric difficulty, truncation-aware scoring/clustering, and forensic analysis (FFT, compression, hazard). Proven on 6.5B tokens across 75+ models—ready to use today.
We fix the biggest evaluation blind spots
Eight systemic problems in current LLM evaluation—solved with an information-processing pipeline.
Parametric manifolds
Coordinate-based generation produces infinite, contamination-proof tests with controllable length, depth, interference, and format.
Per-point + confidence
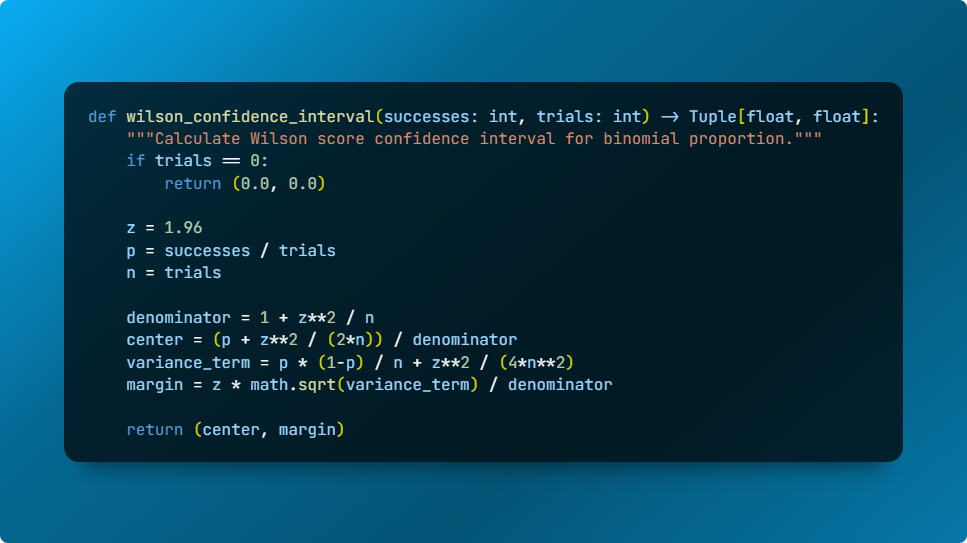
Wilson CIs, excess accuracy, and tiering keep aggregate scores honest and make head-to-head comparisons statistically meaningful.
Forensic signals
FFT, compression, and hazard analyses expose reasoning quality, loops, and thinking budgets—not just final answers.
Truncation + token cost
Truncations are first-class failures; score/token tracks efficiency so "expensive correctness" stops hiding behind averages.
Live tools you can use now
Explore the data, review the code, compare models, and inspect failure boundaries - all directly from your browser.
Analyze without running inference
The 6.5B-token m12x dataset is ready to query. Pull it locally and start exploring reasoning surfaces.
cd reasonscape
curl https://reasonscape.com/data/m12x/m12x.db -o data/m12x.db
python analyze.py evals data/dataset-m12x.json
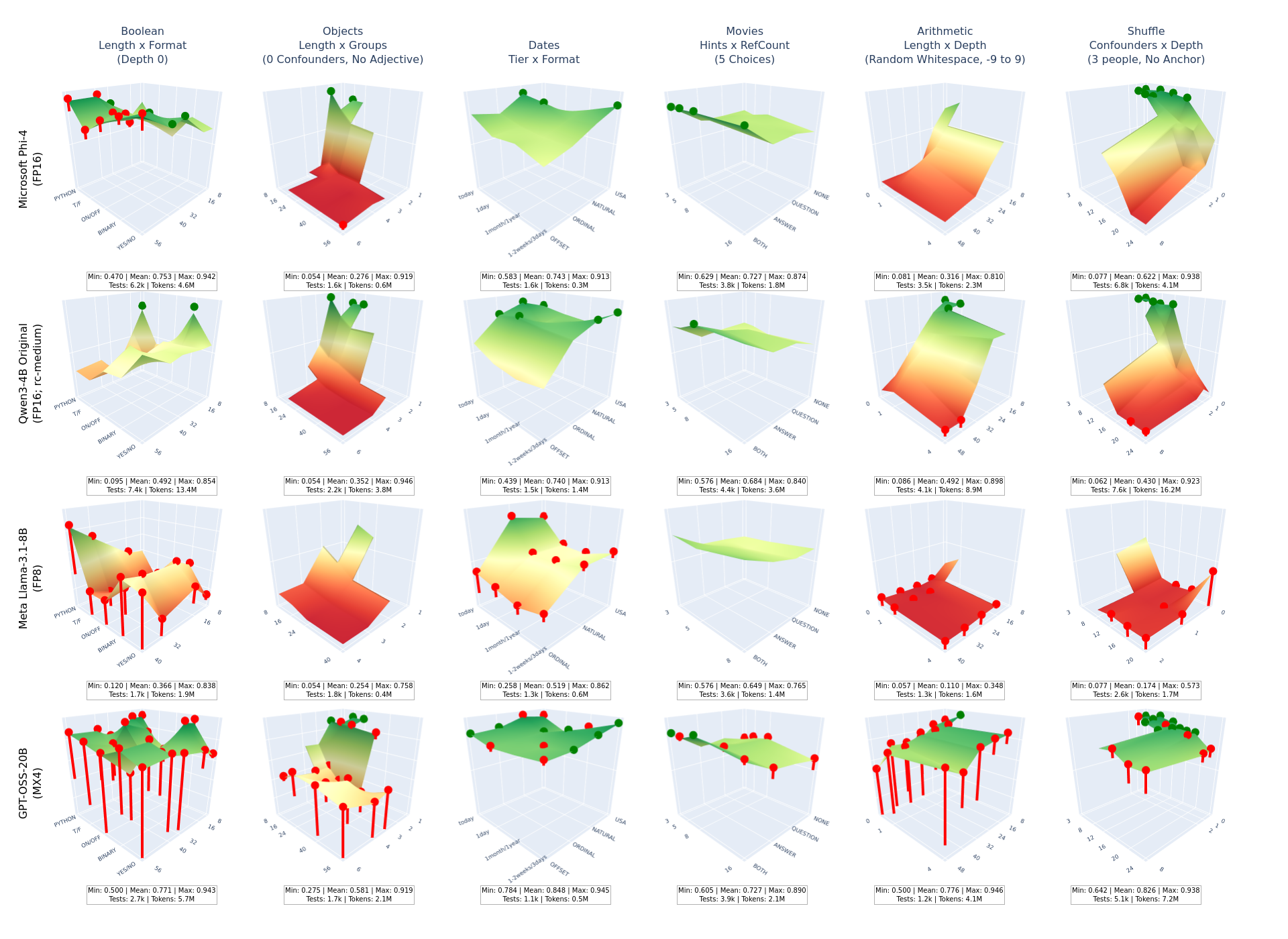
Twelve cognitive domains
Breadth of coverage matters. m12x spans across the core reasoning workloads required for practical Reasoning LLM applications. Click on any card below for detailed information!
Multi-step Math
Length × depth manifolds stress symbolic computation with varying whitespace.
Logical evaluation
Nested expressions expose logic consistency, 5 notations tests format sensitivity.
Structural parsing
Stack discipline and pattern tracking, out-of-domain inputs and outputs.
Selective attention
Categorization and counting under load with distractors.
State tracking
Swap sequences test working memory across length and depth with distractors.
Algorithmic thinking
Ordering and language reasoning, output formatting.
Temporal reasoning
Calendar math and pattern recognition, date format variation.
Character analysis
Symbolic parsing with distractors.
Pattern recognition
Categorization with semantic cues.
Rule-based generation
Instruction following with complex constraints.
Spatial reasoning
SVG Shape recognition under rotation, translation and transformation.
Logistics planning
Absolute and Relative spatial operations with interference.
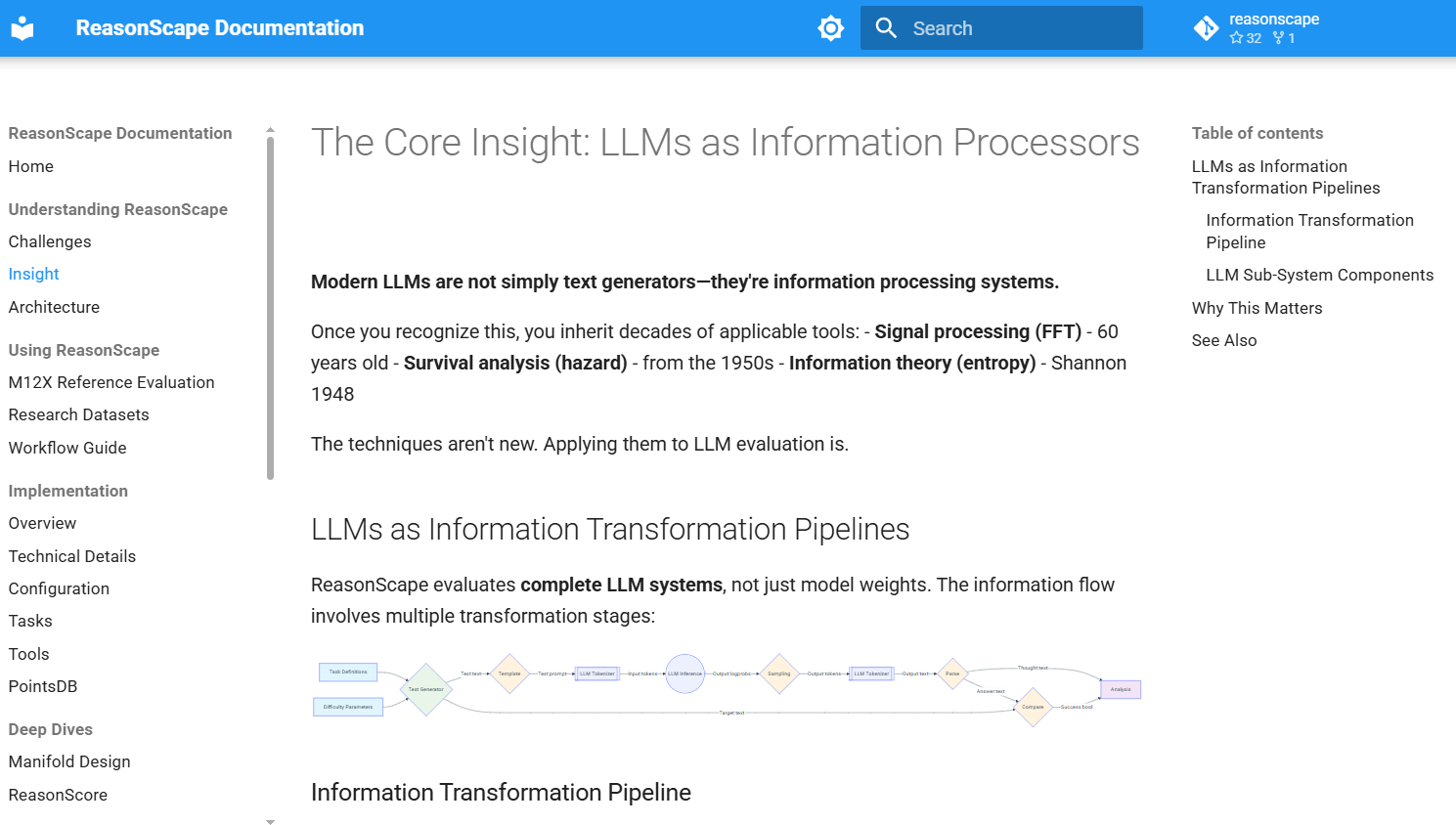
Methodology: Five-stage pipeline
ReasonScape treats LLM evaluation as an information-processing pipeline—from parametric test generation through statistical scoring to forensic root-cause analysis.
Parametric task manifolds; deterministic coordinates.
Adaptive sampling, caching, precision targeting.
Excess accuracy, truncation penalties, tier mapping.
Leaderboard, spider plots, surfaces for pattern finding.
FFT, compression, hazard to explain root causes.
Analysis Tools
Each tool addresses a specific evaluation question—from aggregate ranking to temporal reasoning behavior forensics.
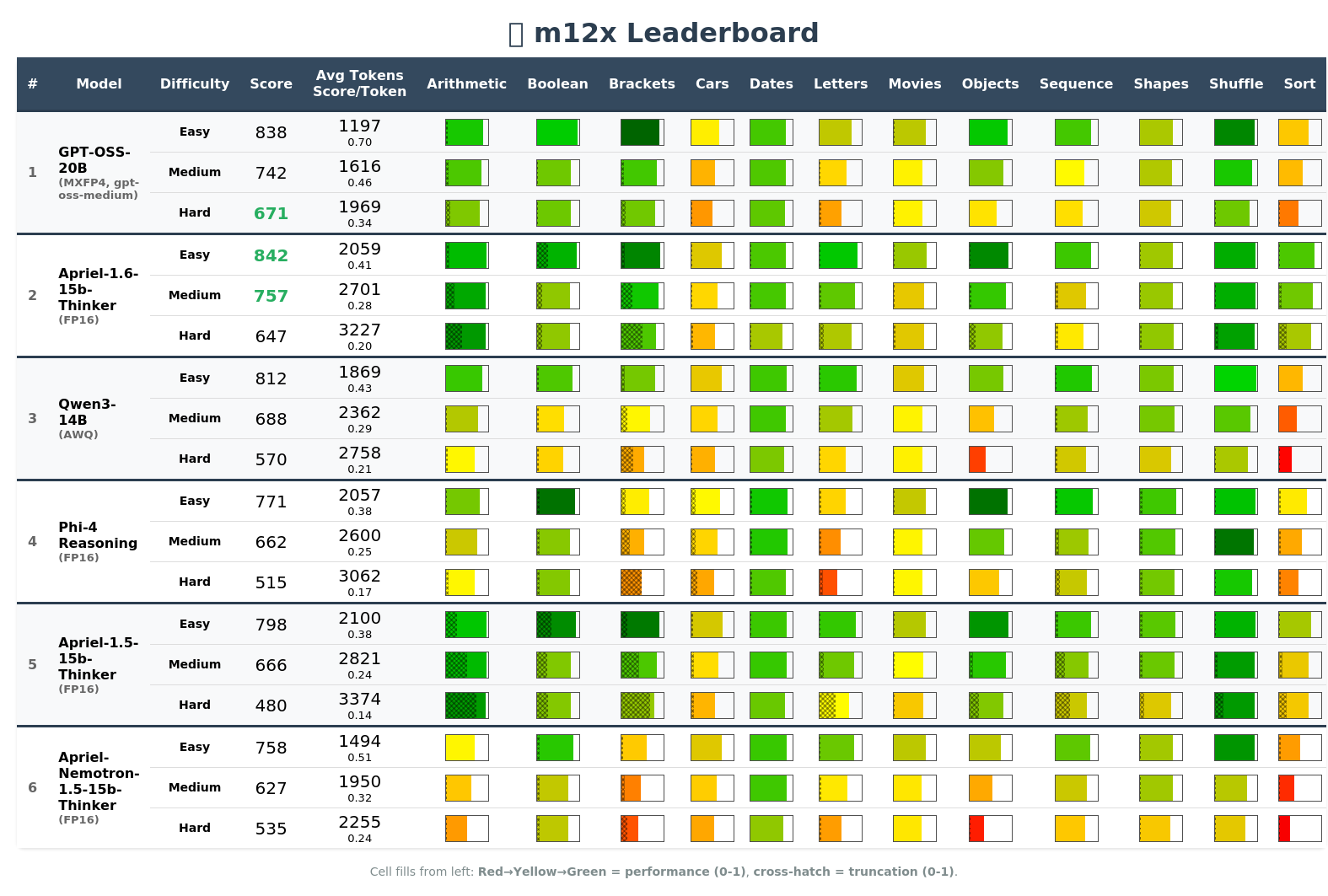
ReasonScore
Unified metric with Wilson CIs, truncation penalties, geometric mean for balance, and score/token efficiency.
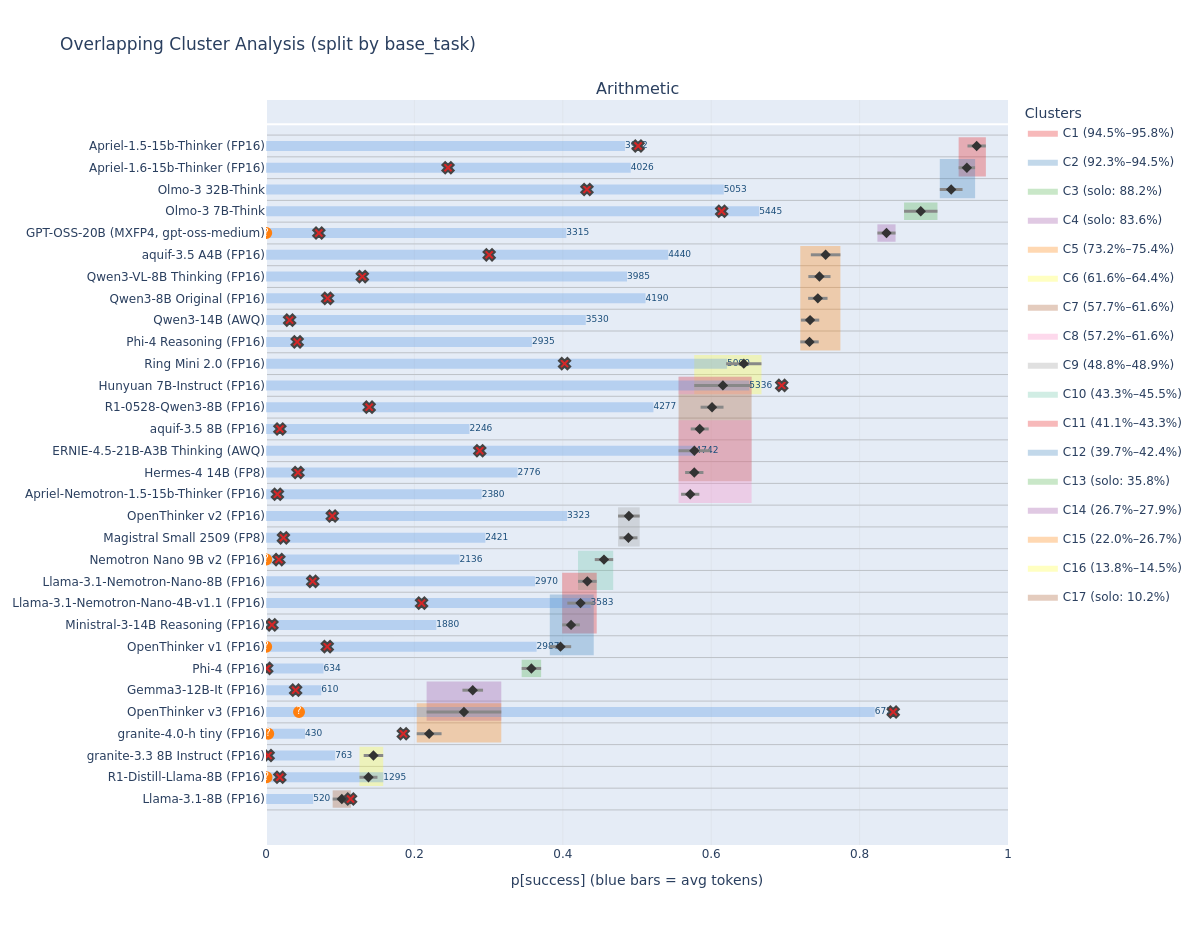
Cluster
Statistical grouping using confidence interval overlap to identify models that are truly indistinguishable.

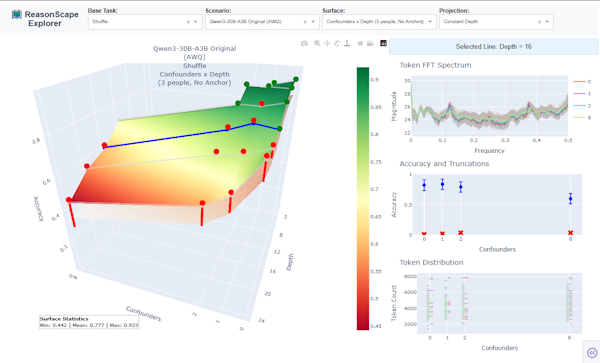
Surface
3D visualization of accuracy across parameter grids to identify capability cliffs and performance boundaries.

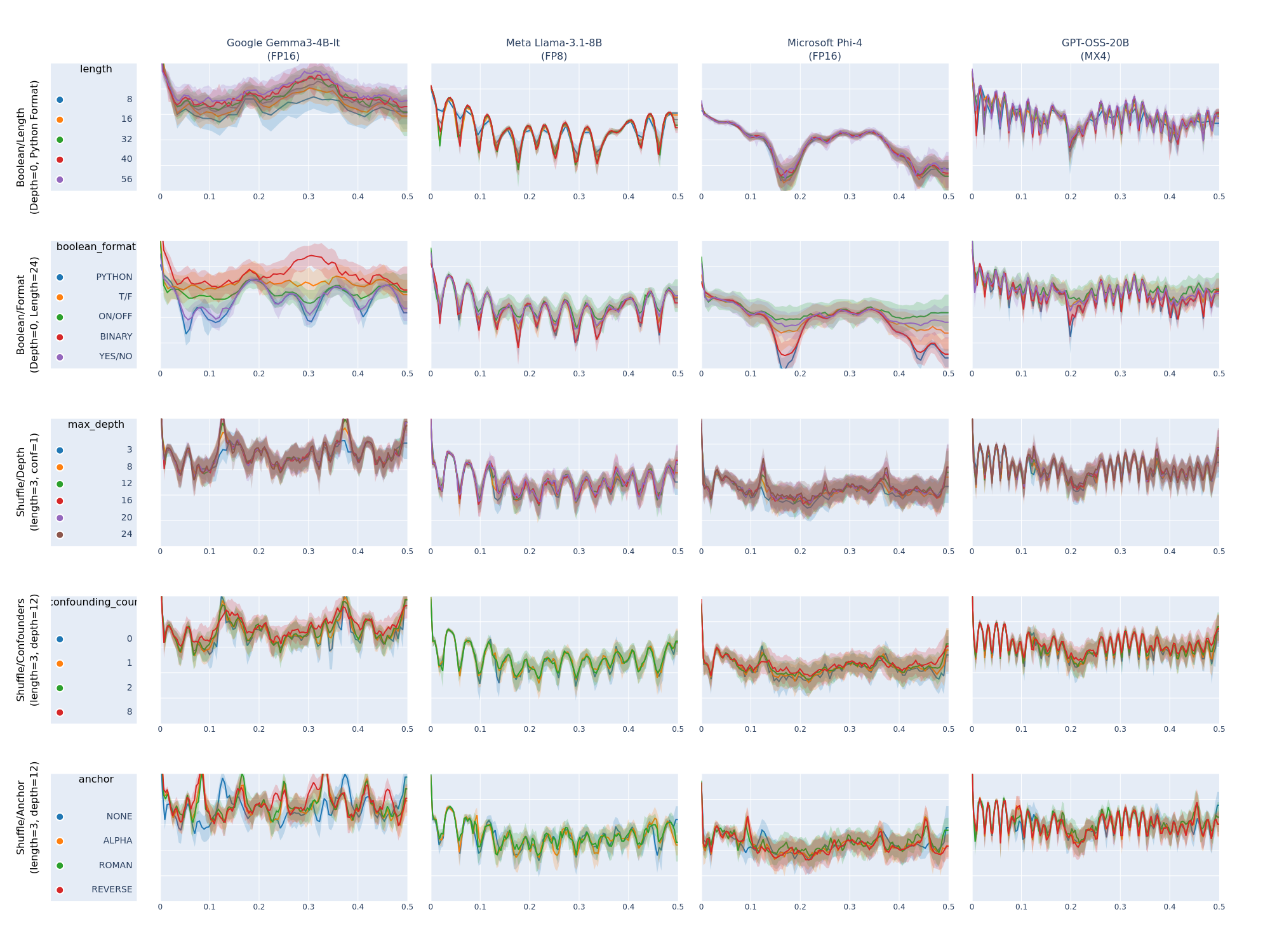
FFT
Frequency domain analysis to distinguish tokenizer effects from model capabilities and output patterns.
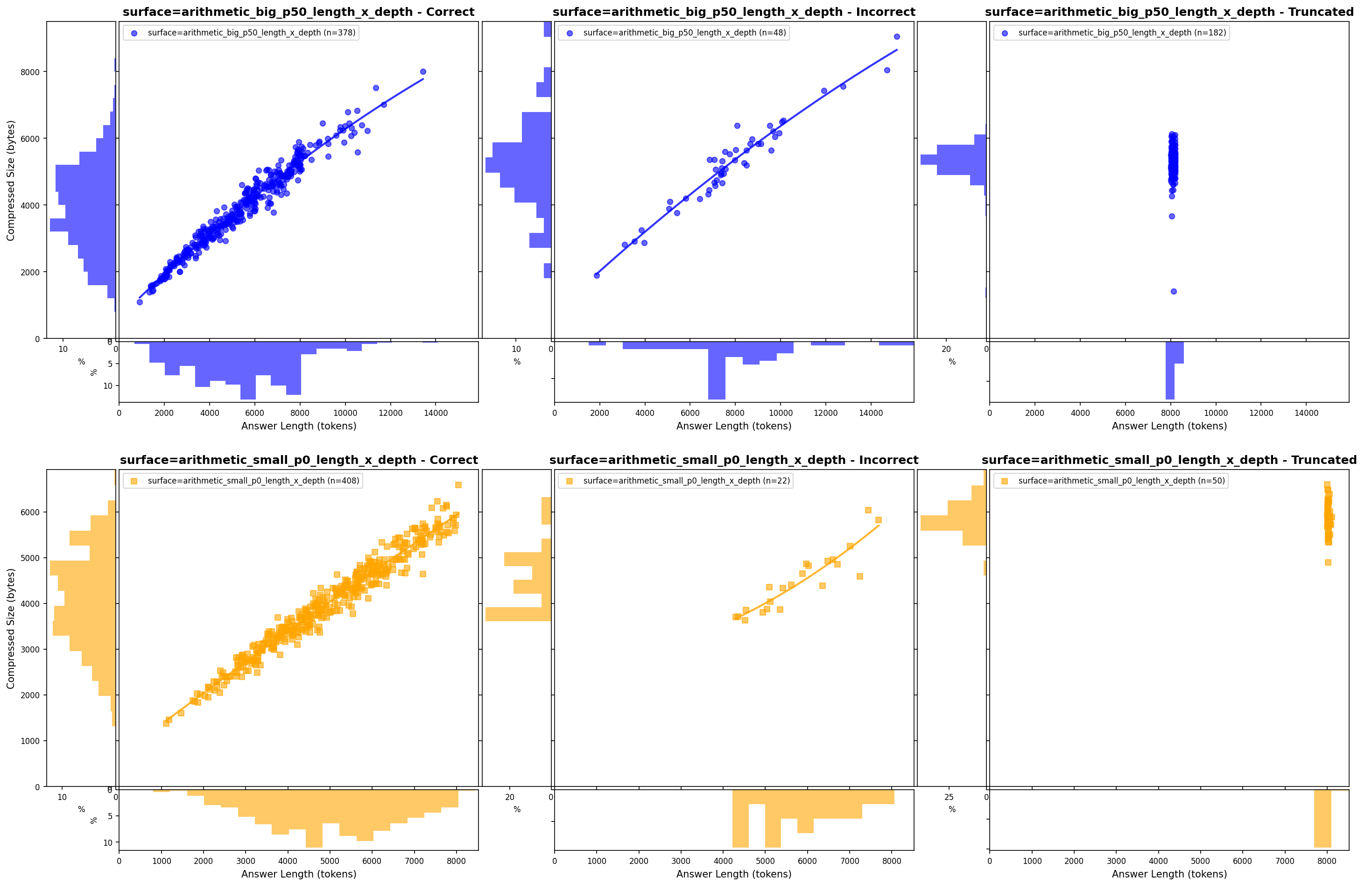
Compression
Information-theoretic analysis revealing underthink/overthink patterns and reasoning loop detection.
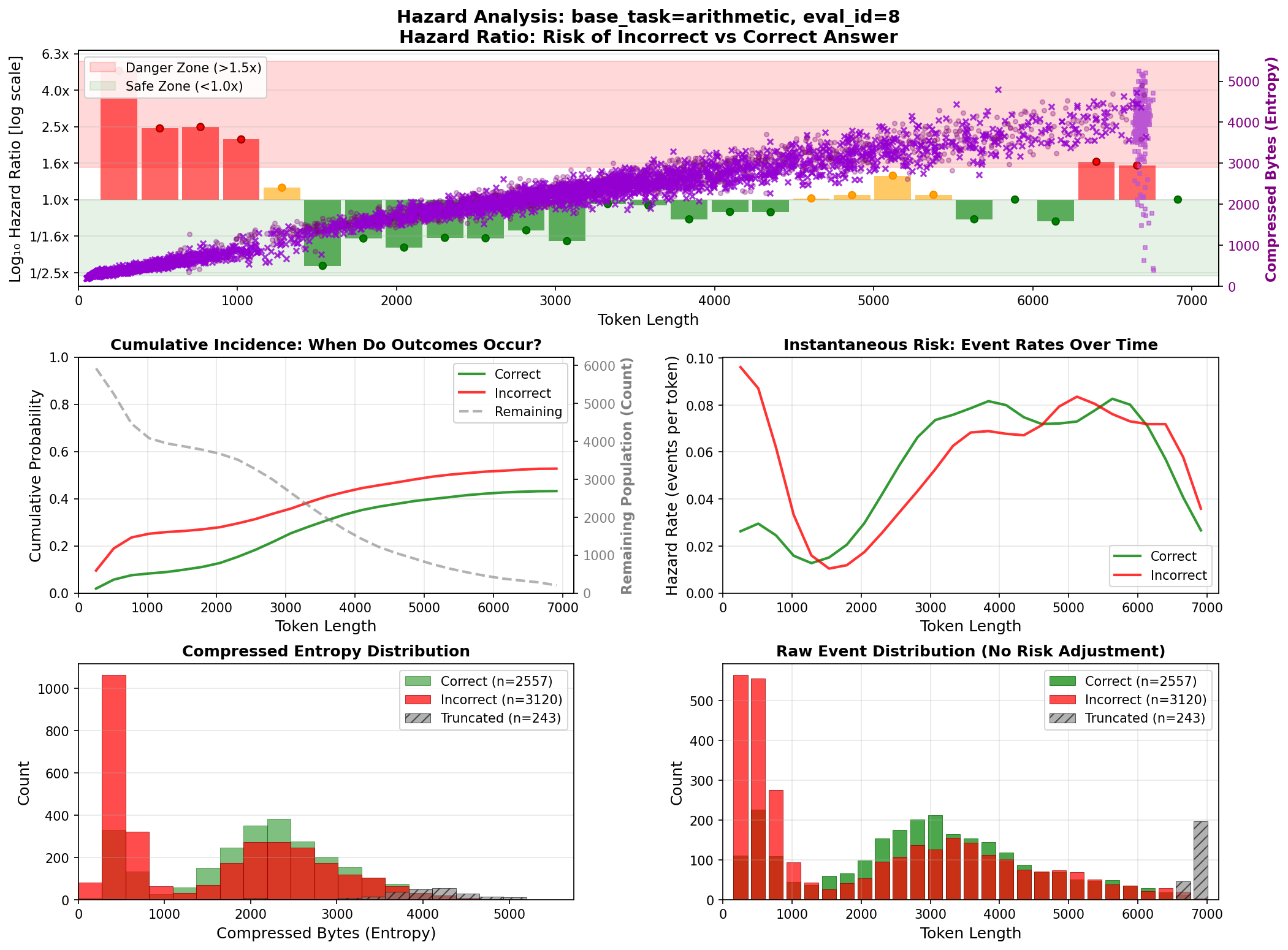
Hazard
Temporal failure analysis showing when and how models fail during token generation.

Four research workflows, one unified platform
ReasonScape supports four distinct research activities - each with different tools, questions, and outcomes.
Ranking & Benchmarking
"What's the best model overall?" — Aggregate rankings with ReasonScore to identify 3-5 candidates for deeper investigation.
Comparative Evaluation
"Which models are truly different?" — Statistical clustering with CI overlap to separate signal from measurement noise.
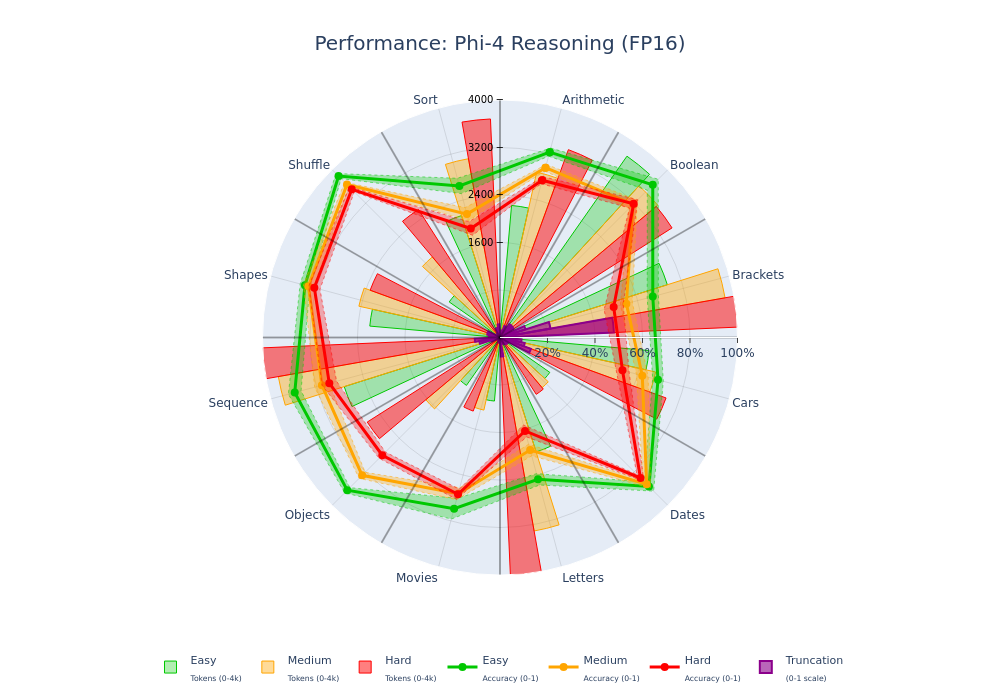
Model Characterization
"What are the trade-offs?" — Profile cognitive fingerprints, capability zones, and cost/performance characteristics.
Failure Diagnosis
"Why/how/when did it fail?" — Root-cause analysis across input, reasoning, output, and temporal dimensions.